Have you ever heard of block explorers and analytics tools for blockchain networks? Or, have you ever wondered how block explorers and analytics tools work for blockchain networks?
What is a block explorer?
Let’s keep it simple!
A blockchain block explorer allows you to browse the blockchain just like a browser or a scanner that gives you your asked information!
It’s a web application or software tool that allows users to view information about blocks, transactions, and addresses on a specific blockchain network. These explorers are specifically designed to interact with the nodes on a blockchain network to extract information about transactions and other data stored in blocks. The information displayed by a blockchain explorer may include transaction histories, addresses, fees, confirmations, NFTs and etc.
They are tools that allow users to access and analyze data on a blockchain, providing a graphical interface to view information about transactions, addresses, and network activity.
Block explorers are especially useful for developers, who use them to debug their code and track the status of their smart contracts, and for traders and investors, who use them to monitor network activity and track the movement of tokens on the blockchain. Block explorers offer a range of useful functions for traders, miners, validators, businesses, and enthusiasts alike.
They enable users to track transactions, view address information, and monitor network activity. Miners can use them to verify successful mining, while businesses can analyze transaction data. Block explorers can also be used to monitor the activity of whales and other prominent users on the blockchain.
Beyond Transparency & Hidden Benefits
- Transaction tracking: Block explorers allow users to view transaction history on the blockchain, including the status, sender, recipient, and value of each transaction.
- Address information: Block explorers allow users to view information about specific addresses on the blockchain, including the balance and transaction history of each address.
- Smart contract monitoring: Block explorers allow users to track the status of smart contracts on the blockchain, including the code, state, and execution history of each contract.
- Network analytics: Block explorers provide users with detailed analytics on the network, including information on block production, network performance, and the distribution of tokens on the blockchain.
- Transparency: Block explorers make blockchain data more transparent and accessible to the public, allowing users to verify transactions and monitor network activity without the need for intermediaries.
- Debugging: Block explorers can be used by developers to debug their code and ensure that it is working properly.
- Security: Block explorers can help users identify fraudulent activity on the blockchain and monitor for potential security threats.
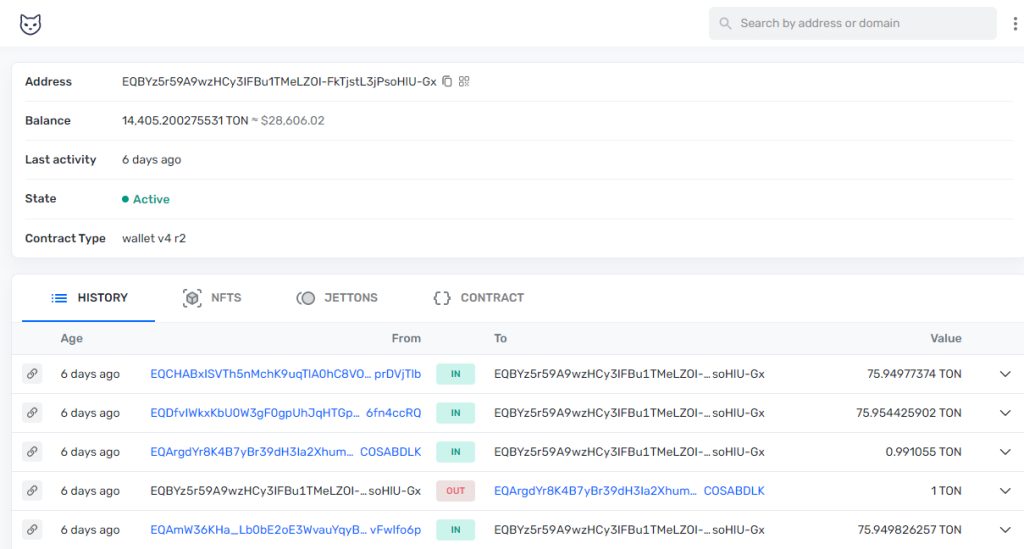
When using a block explorer to search for an address, the process is generally the same across different blockchains. For instance, on a block explorer, the top result displays an address starting with “ٍٍEQCH,” or anything different up to your network; which represents a person’s address in this example. This illustrates the common experience of using a block explorer to find and access information about a specific address.
next, you will see some other info which are easy to follow:
Input and Output:
In a block explorer, the terms “input” and “output” refer to the transaction details displayed for a specific transaction.
The “input” represents the source of the funds or the sender of the transaction. It typically includes information such as the sender’s address, the amount of cryptocurrency being sent, and any additional data associated with the input.
On the other hand, the “output” represents the destination of the funds or the recipient of the transaction. It provides details about the recipient’s address, the amount of cryptocurrency received, and any additional data associated with the output.
These input and output sections in a block explorer provide visibility into the flow of funds and help users track the movement of transactions within a blockchain network.
Balance: typically refers to the amount of cryptocurrency held in a specific address or wallet.
Last activity: refers to the most recent transaction or activity associated with a specific address. It indicates the date and time of the latest transaction or interaction involving that address.
State: typically refers to the status or condition of a smart contract or address. It can provide information about whether the contract is active, inactive, or terminated. For an address, the state may indicate whether it is a valid or known address within the blockchain network.
Contract type: refers to the classification or categorization of a smart contract on the blockchain. It helps identify the purpose or functionality of the contract. For example, a contract may be categorized as a token contract, decentralized finance (DeFi) contract, or non-fungible token (NFT) contract, among others.
Types Of Explorers:
Before talking about types,
lets know the main ones and their differences!
| Analysis | Dedicated Explorers | General Explorers |
| Purpose | Explore specific & Tailored features for blockchain networks | Explore multiple blockchain networks |
| Focus | Detailed information and analysis of transactions, blocks, etc. | Broad view of different blockchains and associated data |
| Data Coverage | In-depth insights within a specific blockchain ecosystem | High-level view across various blockchain networks |
| User Base | Users seeking detailed information within a specific blockchain | Users interested in exploring and comparing multiple chains |
| Utility | Blockchain-specific analysis, research, and monitoring | Cross-chain comparisons, portfolio management, and tracking multiple assets |
| Dev Tools | Provides additional tools for developers, such as API access, smart contract interaction, and network statistics | Limited developer-centric tools compared to blockchain-specific explorers |
| Community & Support | Often backed by a dedicated community and comprehensive support resources | May have more limited community support due to the broader focus across multiple networks |
Other than these there are some major explorer types:
Full Node Explorers: These are the most common and widely used type of blockchain explorer, as they allow users to access the full transaction history of the blockchain network.
Indexing Explorers: These explorers are also quite popular, as they provide faster access to data by indexing and storing it in a separate database.
API-Based Explorers: These explorers are commonly used by developers, as they provide easy access to blockchain data through APIs provided by the blockchain network.
Multi-Chain Explorers: These explorers are gaining popularity among users who want to view and analyze data from multiple blockchains in a single platform.
Token/NFT Explorer: These are specialized explorers focused on providing information about tokens and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). It allows users to view details such as token balances, transaction histories, and metadata associated with specific tokens or NFTs. These explorers are valuable tools for token holders, collectors, and investors to track and explore the token and NFT ecosystem on the blockchain.
Popular Ones:
TonScan: TON (The Open Network) blockchain.
Etherscan: Ethereum network.
Tronscan: TRON network
Solscan: Solana network
In conclusion,
block explorers are the key to unlocking the mysteries of the blockchain. With their transparency, transaction tracking, and smart contract analysis, they empower users to navigate the decentralized world with confidence.




